SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is a comprehensive environment that allows easy access to all the components of SQL Server and database for configuring, administering, and managing all its components. A central feature of SSMS is the Object Explorer, which allows the user to browse, select, and act upon any of the objects within the server.
It comprises of a wide range of graphical tools with several script editors that can be used by administrators and developers irrespective of their skill levels. SSMS is a single environment with a combination of all the features and functionalities available in the previous versions of SQL Server, so developers and database administrators can make the most of the familiar features and rich scripting capabilities.
This is a standalone tool that empowers the tooling team to be faster and efficient. It is a fantastic solution for enterprises managing several servers on different versions and is also compatible with Azure components like Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Azure SQL Database.
SQL Server Management Studio is a software application first launched with Microsoft SQL Server 2005 that is used for configuring, managing, and administering all components within Microsoft SQL Server. The tool includes both script editors and graphical tools which work with objects and features of the server.
It also shipped a separate Express edition that could be freely downloaded, however recent versions of SSMS are fully capable of connecting to and manage any SQL Server Express instance. Microsoft also incorporated backwards compatibility for older versions of SQL Server thus allowing a newer version of SSMS to connect to older versions of SQL Server instances.
Starting from version 11, the application was based on the Visual Studio 2010 shell, using WPF for the user interface.
In June 2015, Microsoft announced their intention to release future versions of SSMS independently of SQL Server database engine releases.
About Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft using Structured Query Language (SQL, often pronounced “sequel”). As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network (including the Internet). Microsoft markets at least a dozen different editions of Microsoft SQL Server, aimed at different audiences and for workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications with many concurrent users.
Milestones
- MS SQL Server for OS/2 began as a project to port Sybase SQL Server onto OS/2 in 1989, by Sybase, Ashton-Tate, and Microsoft.
- SQL Server 4.2 for NT is released in 1993, marking the entry onto Windows NT.
- SQL Server 6.0 is released in 1995, marking the end of collaboration with Sybase; Sybase would continue developing their own variant of SQL Server, Sybase Adaptive Server Enterprise, independently of Microsoft.
- SQL Server 7.0 is released in 1998, marking the conversion of the source code from C to C++.
- SQL Server 2000, released in 2000. SQL Server 2000 SQL Server 8 SQL Server 8.0 codename Shiloh Release date: 2000-11-30.
- SQL Server 2005, released in 2005, finishes the complete revision of the old Sybase code into Microsoft code.
- SQL Server 2008, released in 2008, supports hierarchical data, adds FILESTREAM and SPATIAL data types.
- SQL Server 2012, released in 2012, adds columnar in-memory storage aka xVelocity.
- SQL Server 2017, released in 2017, adds Linux support for these Linux platforms: Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, Ubuntu & Docker Engine.
- SQL Server 2019, released in 2019, adds Big Data Clusters, enhancements to the “Intelligent Database”, enhanced monitoring features, updated developer experience, and updates/enhancements for Linux based installations.
- SQL Server 2022, released in 2022.
Currently
As of January 2025, the following versions are supported by Microsoft:
- SQL Server 2016
- SQL Server 2017
- SQL Server 2019
- SQL Server 2022
From SQL Server 2016 onward, the product is supported on x64 processors only and must have 1.4 GHz processor as a minimum, 2.0 GHz or faster is recommended.
Comparison of database tools
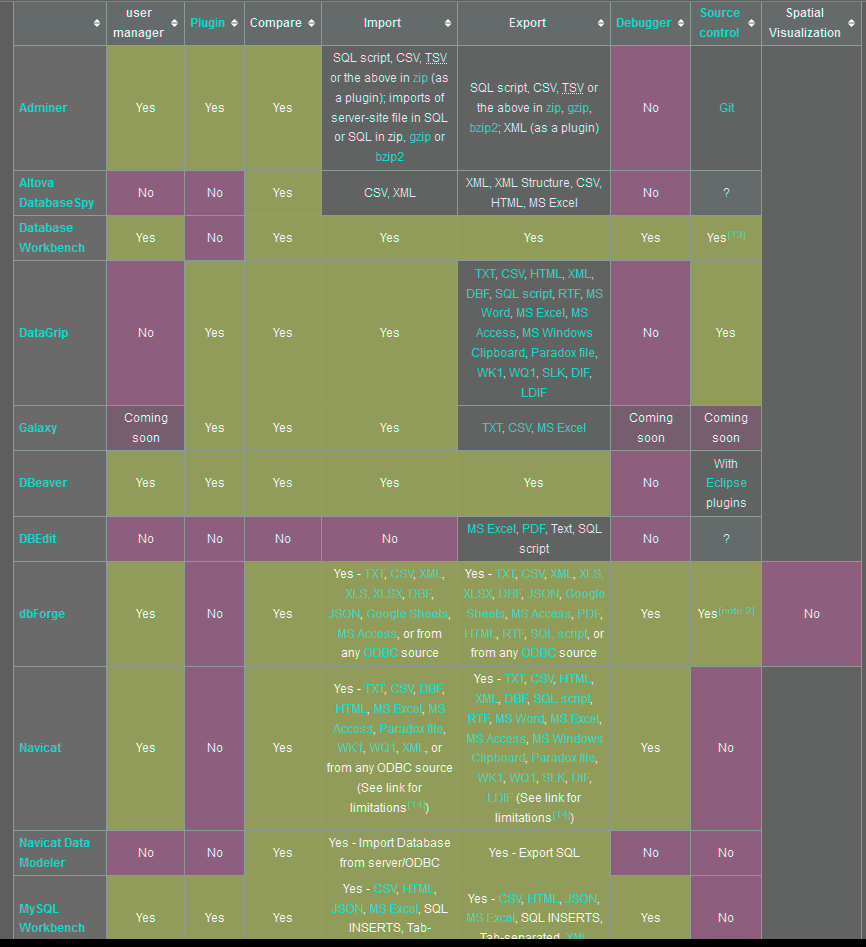
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available database administrator tools. Please see individual product articles for further information. This article is neither all-inclusive nor necessarily up to date.
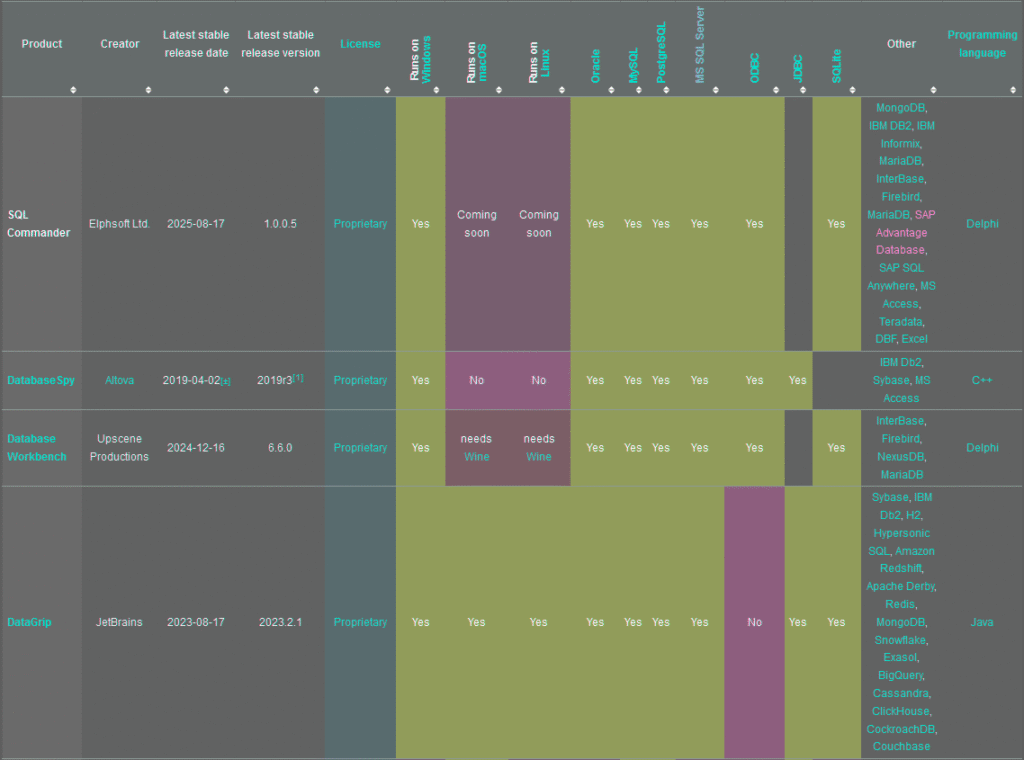
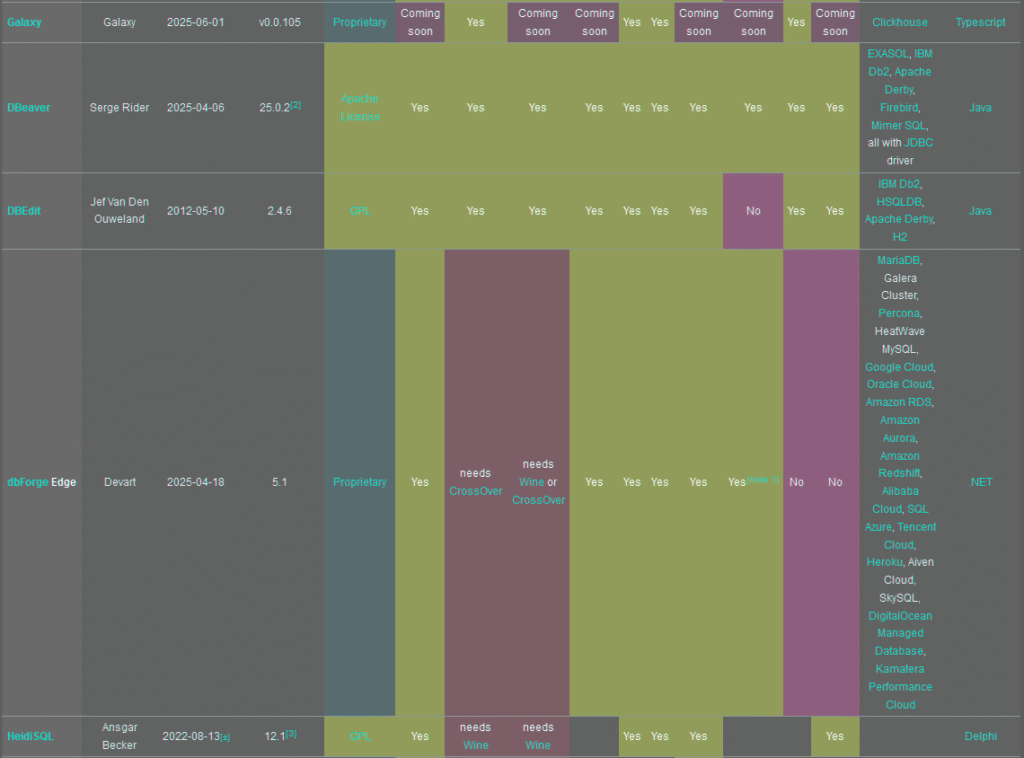
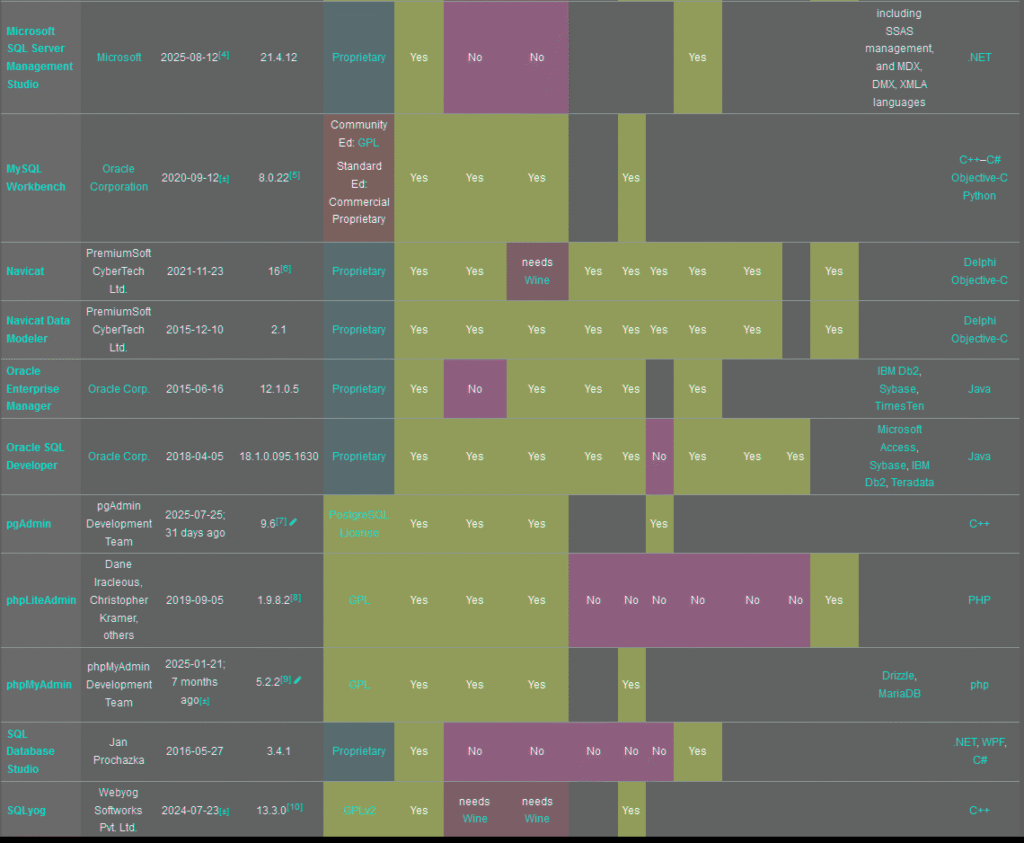
Legend
- User Interface:
- Browser based – executes on a computer server and is accessed via a network using a web browser
- desktop – executes on a personal computer
- Create/alter table:
- Yes – can create table, alter its definition and data, and add new rows
- Some – can only create/alter table definition, not data
- Browse table:
- Yes – can browse table definition and data
- Some – can only browse table definition
- Multi-server support:
- Yes – can manage from the same window/session multiple servers
- Some – can manage from a different window/session multiple servers
- Monitoring server:
- Yes – includes a headless server, that runs checks and reports failures
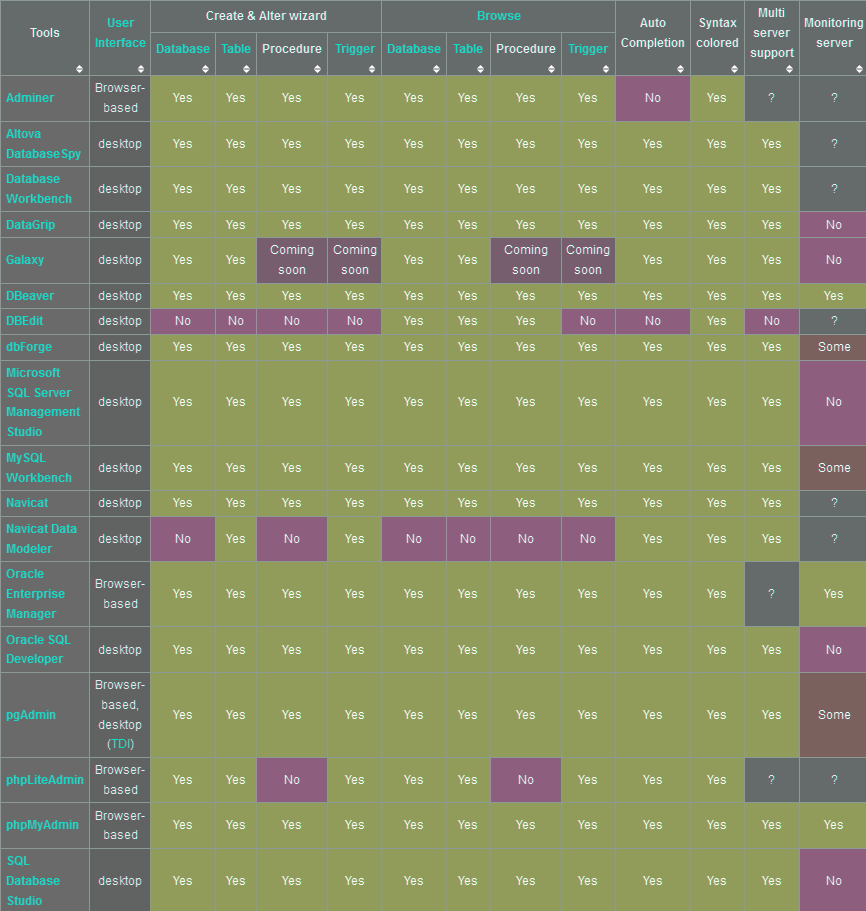
Legend:
- User manager:
- Yes – user manager with support for database and schema permissions as well as for individual object (table, view, functions) permissions
- Some – simple user manager with support for database and schema permissions
- No – no user manager, or read-only user manager
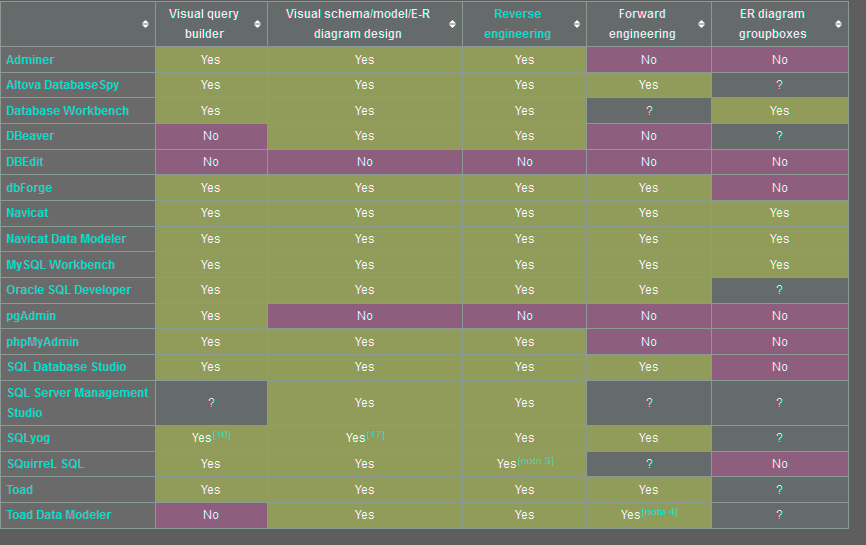
Features – visual design and reverse engineering
Legend:
- Visual schema/E-R design: the ability to draw entity-relationship diagrams for the database. If missing, the following two features will also be missing
- Reverse engineering – the ability to produce an ER diagram from a database, complete with foreign key relationships
- Yes – supports incremental reverse engineering, preserving user modifications to the diagram and importing only changes from the database
- Some – can only reverse engineer the entire database at once and drops any user modifications to the diagram (can’t “refresh” the diagram to match the database)
- Forward engineering – the ability to update the database schema with changes made to its entities and relationships via the ER diagram visual designer
- Yes – can update user-selected entities
- Some – can only update the entire database at once
Notes
- Only for Data Import/Export features.
- Only for SQL Server and MySQL/MariaDB.
- Only incremental, by manually going through each table and clicking “Add to graph”.
- Generated SQL must be executed outside Toad Data Modeler.
